The Web Chart: Visualisation
CHAPTER 8
The internet connectivity Diagram:
The above diagram shows an internet connectivity pathway to your home devices using Satellite internet technology.
Know more about internet connectivity >>>
Physical Devices in Internet Connectivity:
- Smart Phone, PC, Laptop
- Wireless Access Point
- Modem
- Router
- Satellite Dish
- Satellite
A WAP (short for Wireless Access Point) is a device that connects wireless devices to a wired network via Wi-Fi.
A Firewall is a security system within Router that monitors and controls incoming and outgoing network traffic.
A Router is a device that direct traffic between the home devices and web.
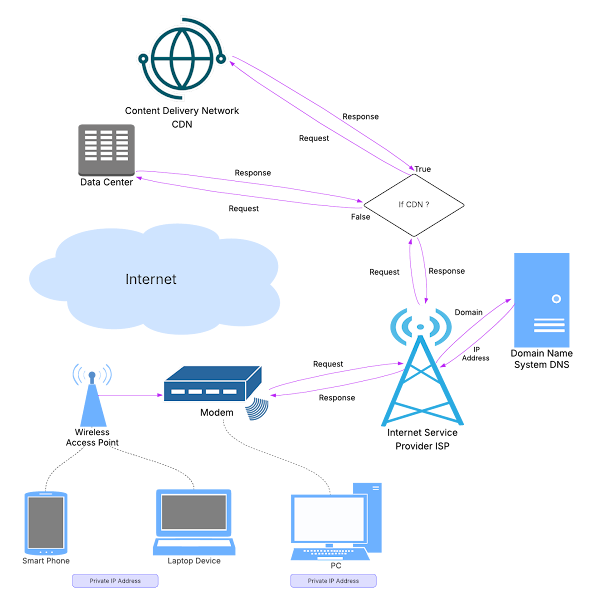
The Web Chart describing the Request - Response cycle:
Terminologies:
- ISP (Internet Service Provider)
- DNS (Domain Name System)
- CDN (Content Delivery Network)
- IP Address
- Domain
- Request and Response
You might’ve seen these terminologies before!
If you would like a quick refresher, please go back to the Story of Web >>> — our main blog that walks you through everything, one chapter at a time.
🎉 Fun Fact: The Internet Is (Very) Real and Wired!
Even though browsing the web feels like a smooth, invisible experience — as if everything just floats in from the "cloud" — the truth is that the internet is built on a massive network of real, physical infrastructure.
Most of the communication that happens between your browser (your device) and a server (powerful computers sitting in physical data centers) travels through cables (fibre optic / coaxial cables) that run underground, across cities, and even under the ocean. Yep, there is literal cable sitting in the bottom of the ocean, making sure your messages get to the right place.
Sure, satellites do exist, but they’re mostly used in remote areas. Most day-to-day internet usage happens right here on Earth — at light speed, through wires.⚡🌍

.png)
.jpg)
Comments
Post a Comment
Enter you valuable comments